Archives

- Issue 4, Volume 9, 2025
- Issue 3, Volume 9, 2025
- Issue 2, Volume 9, 2025
- Issue 1, Volume 9, 2025
- Issue 4, Volume 8, 2024
- Issue 3, Volume 8, 2024
- Issue 2, Volume 8, 2024
- Issue 1, Volume 8, 2024
- Issue 4, Volume 7, 2023
- Issue 3, Volume 7, 2023
- Issue 2, Volume 7, 2023
- Issue 1, Volume 7, 2023
- Issue 4, Volume 6, 2022
- Issue 3, Volume 6, 2022
- Issue 2, Volume 6, 2022
- Issue 1, Volume 6, 2022
- Issue 4, Volume 5, 2021
- Latest Articles
- Articles of 2024-2025

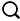






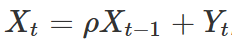 , where
, where 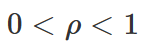 and the errors Yt are independent random variables following an exponential distribution of parameter θ. To achieve this, a Bayesian Autoregressive Adaptive Refined Descriptive Sampling (B2ARDS) algorithm is proposed to estimate the parameters ρ and θ of such a model by a Bayesian method. We have used the same prior as the one already used by some authors, and computed their properties when the Normality error assumption is released to an exponential distribution. The results show that B2ARDS algorithm provides accurate and efficient point estimates.
and the errors Yt are independent random variables following an exponential distribution of parameter θ. To achieve this, a Bayesian Autoregressive Adaptive Refined Descriptive Sampling (B2ARDS) algorithm is proposed to estimate the parameters ρ and θ of such a model by a Bayesian method. We have used the same prior as the one already used by some authors, and computed their properties when the Normality error assumption is released to an exponential distribution. The results show that B2ARDS algorithm provides accurate and efficient point estimates.




 loading......
loading......